Android USB Connections MTP, PTP & USB Mass Storage
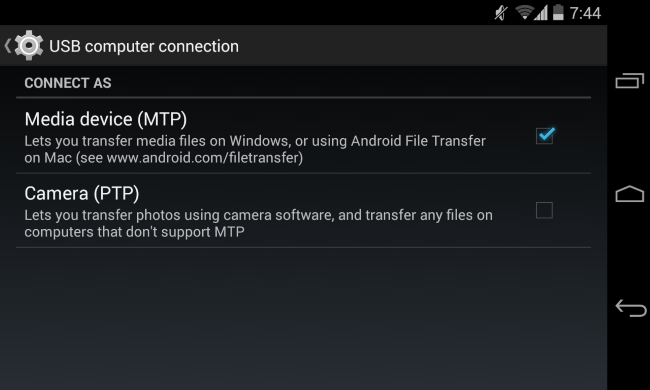
Whenever you connect an Android device to your computer, it asks how this device should be seen by the computer (MTP or PTP protocol). Older Android devices may ask for USB mass storage - used to transfer the files to and from the computer. You can choose the connection method by opening the Settings app -> select Storage -> click the menu button -> select USB computer connection. From this menu you can choose the protocol used for communication when the device is connected to a computer via USB cable.
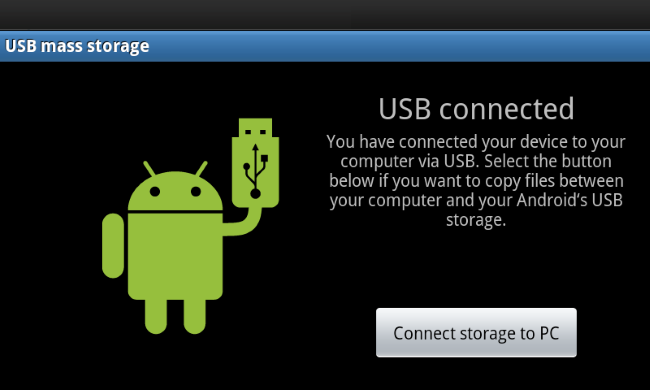
Why you cannot use USB Mass Storage anymore ?
The USB mass storage mode, was the older version of Android to connect to an external device. Usually when you had to connect your Android device to a computer you had to tap the “Connect storage to PC” in order to make the Android storage accesible to the computer.
As well, when you disconnected the device from the computer you had to tap “Turn off USB storage”. However, there was an issue with this method of accessing files. When the computer was reading files stored on the SD card, these files was unavailable to the Android device itself.
System files was separated within two folders “/data” for system storage and “/sdcard” for USB storage on the same memory support. Usually the installed apps and system files goes to “/data” and the user data along with pictures and other media files on the “/sdcard”.
This method leave the user itself with too little space for downloaded apps. These partitions couldn’t be resized without interfering with the Android system itself (rooting the device). Newest Android versions use different USB connection protocols to avoid data corruption.
What the MTP stands for?
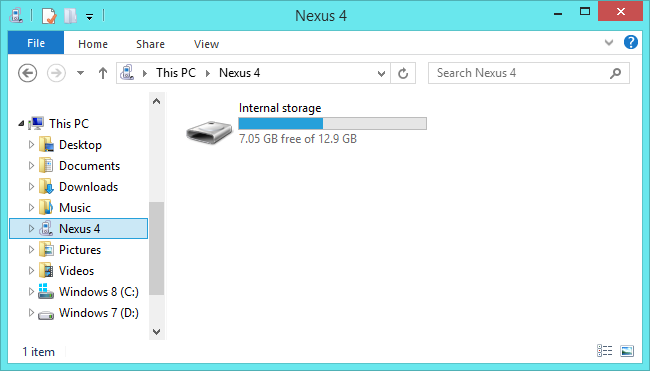
MTP - meaning “Media Transfer Protocol”. When this protocol is selected, the Android appear connected to the computer as a media device. This protocol ensure that the user can access the files stored on the Android device without exposing the Android raw files to Windows. When you start uploading a file to your device using this protocol, the device itself choose to save it.
Also, the file systems are hidden by default and cannot be tampered.
The MTP protocol is supported in both Windows and Linux. The MTP is just a layer of file interpretation between your operating system and Android itself. All the requests you made (for deleting, download or upload) goes through this protocol which interpret and run or refuse the command.
What PTP protocol stands for ?
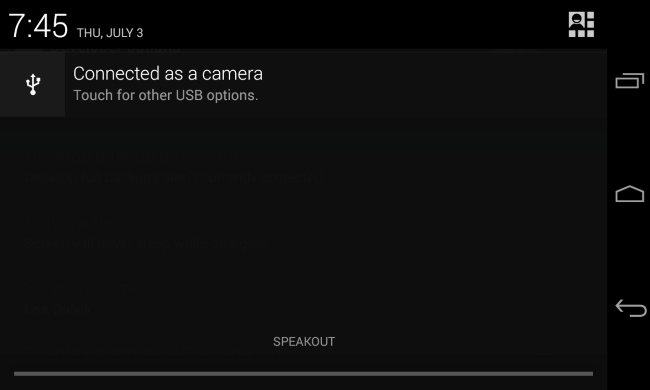
PTP is nothing more than “Picture Transfer Protocol”. When you select this protocol, you will use the Android device as a camera.
Actually MTP is based on PTP but comes with more features and extend the fun ![]()
PTP can interact with any software that grab photos from a digital camera. PTP is basically a protocol for communication with digital cameras. You can use the PTP mode to transfer the photos from your Android phone or tablet without any other special software installed.
In the end, it’s up to you how you want to transfer the files from the Android device to your computer. It’s even better to use the SD card connected directly do your computer (if you do have something like that). Otherwise use the appropiate protocol to transfer the files to and from your computer.

Pixel 3, Android 10
There is no “USB computer connection” option when I follow your directions. I’ve been struggling with how to move pictures via USB and Bluetooth. Once, I found PTP in a pull-down “window shade” at the top and transferred pictures. Other times I found it and it was not selectable. I don’t find it every time I look.
Any advice?
Thank you.
Will